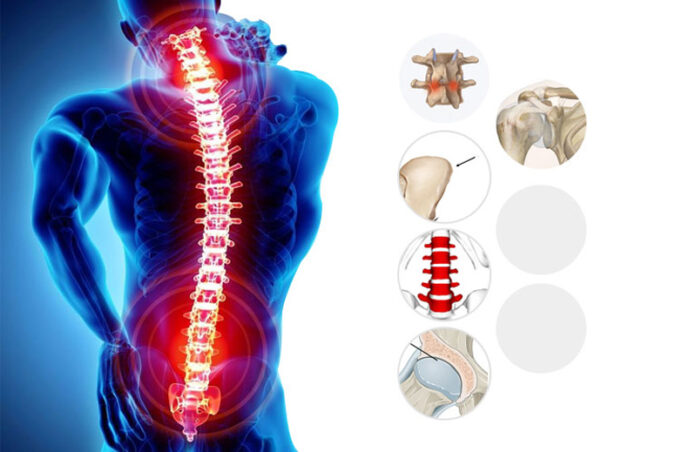
What is ankylosing spondylitis?
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of chronic inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac (SI) joints. It is the spinal fusion process that results in spinal stiffness and immobility. It curves the spine. If the ribs are affected, breathing may also become difficult.
Who can get ankylosing spondylitis?
Anyone can get ankylosing spondylitis, although it is more common in men than women. Symptoms of this disease usually appear between the ages of 17 and 45 years. Ankylosing spondylitis is a genetic disease that can run in families.
Symptoms:
1. Pain and stiffness in the back, which is worse in the morning after waking up and on walking
decreases.
2. Progressive loss of spinal mobility, resulting in spinal stiffness.
3. Sacroiliac joint pain, lower back and hip pain and stiffness.
5. Enthesitis, which is inflammation where a tendon or ligament attaches to a bone.
6. Fatigue and decreased physical activity levels.
7. Uveitis or inflammation of the middle layer of the eye.
8. Psoriasis
Reason:
Ankylosing spondylitis has no specific cause, although genetic factors appear to be involved. In particular, people with the HLA-B27 gene have a higher risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis. However, only some people with the gene develop the disease.
Diagnosis:
1. history
2. Physical exam Imaging scan: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans can usually detect spinal problems earlier than X-rays.
3. Blood tests: Blood tests can check for the presence of the HLA-B27 gene.
Complications:
1. Stinging of the vertebrae (ankylosis).
2. Kyphosis (forward curvature of the spine).
3. Osteoporosis (bone loss).
4. Painful eye inflammation (iritis or uveitis) and sensitivity to light (photophobia).
5. Heart disease, including aortitis, arrhythmias and cardiomyopathy.
6. Chest pain that affects breathing.
7. Inflammation of the jaw.
8. Cauda equina syndrome
To do:
Treatment:
*Medication:
1. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
2. Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMRD)
3. Steroidal therapy.
Surgery:
A small number of people with ankylosing spondylitis may need surgery. the joint
Replacement surgery involves implanting an artificial joint. Correction of curved spine by kyphoplasty
is
*Physiotherapy and rehabilitation treatment:
1. Stretching exercises: Gentle stretching exercises to maintain spinal mobility and prevent stiffness
helps
2. Strengthening exercises: Target the muscles that support the spine
Strengthening exercises help improve posture and reduce pain.
3. Aerobic Exercise: Light aerobic exercise like cycling, swimming improves heart fitness and overall
Very effective in improving health.
4. Improves Posture: Correct posture helps reduce pain and prevent sprains
can do A physiotherapy doctor teaches the patient proper posture and body mechanics
can
5. Breathing exercises to reduce stress and anxiety.
7. Electrotherapy
8. Manual therapy